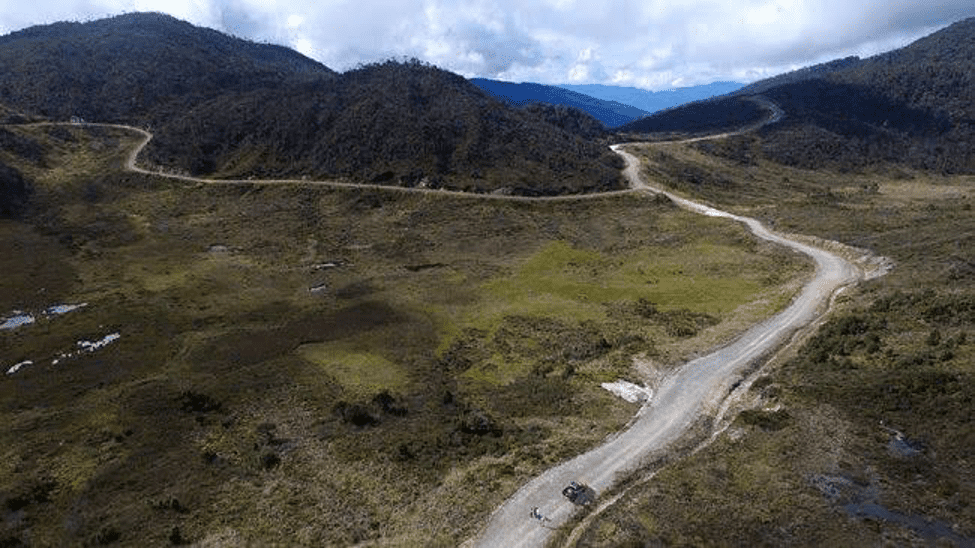
The Trans Papua project is one of the largest infrastructure development initiatives ever undertaken in Indonesia, especially in the Papua region. To connect various areas in Papua that were previously difficult to reach, the project is expected to bring significant changes to the economy and welfare of local communities. However, the impacts are diverse, involving economic, social, and environmental aspects.
One of the main positive impacts of the Trans Papua Project is the increased accessibility between regions. Before the project, many areas in Papua were only accessible by air or sea, at a very high cost. The Trans Papua Road opens up land access, making the distribution of goods and services more efficient and cheaper. Delivery of staples, crops, and other goods becomes faster and more affordable, which in turn lowers the price of goods in rural areas.
The existence of roads that connect various regions also encourages local economic growth. Farmers and fishermen now have easier access to a wider market, increasing their income. In addition, the tourism potential in Papua, which is rich in natural and cultural beauty, can also be better explored with adequate road infrastructure, opening up new business opportunities in the tourism sector.
In terms of welfare, the construction of the Trans Papua road has brought positive changes in access to basic services such as education and health. Many remote villages that were previously difficult to reach can now get better access to health facilities and schools. This has a direct impact on improving people’s quality of life, reducing maternal and child mortality, and increasing education participation rates.
The project also created new jobs, both in the infrastructure development itself and in the sectors affected by the development. Many local people are involved in the project, gaining new skills and increasing their income.
However, despite the positive impacts, the project also poses some challenges and negative effects. Road construction in pristine areas often has the potential to damage the environment. Deforestation and degradation of natural habitats are serious issues that can threaten Papua’s biodiversity. In addition, changes in land use for road construction can disrupt the traditional livelihoods of indigenous communities who rely heavily on the forest and surrounding nature.
On the other hand, accelerated development is often accompanied by a lack of careful planning. Some infrastructure projects may not fully consider the social and cultural impacts on local communities. Social tensions can arise when development is not carried out with an inclusive approach, involving indigenous communities in the planning and implementation process.
The Trans Papua project has great potential to drive economic growth and improve the welfare of communities in Papua. By connecting previously isolated areas, the project provides access to markets, basic services, and new economic opportunities.
However, environmental and social challenges need to be taken seriously for the development to be truly sustainable and beneficial for all parties. An inclusive approach, involving local communities in every stage of development, as well as protection of the natural environment, must be prioritized so that the benefits of this project can be felt optimally and sustainably.