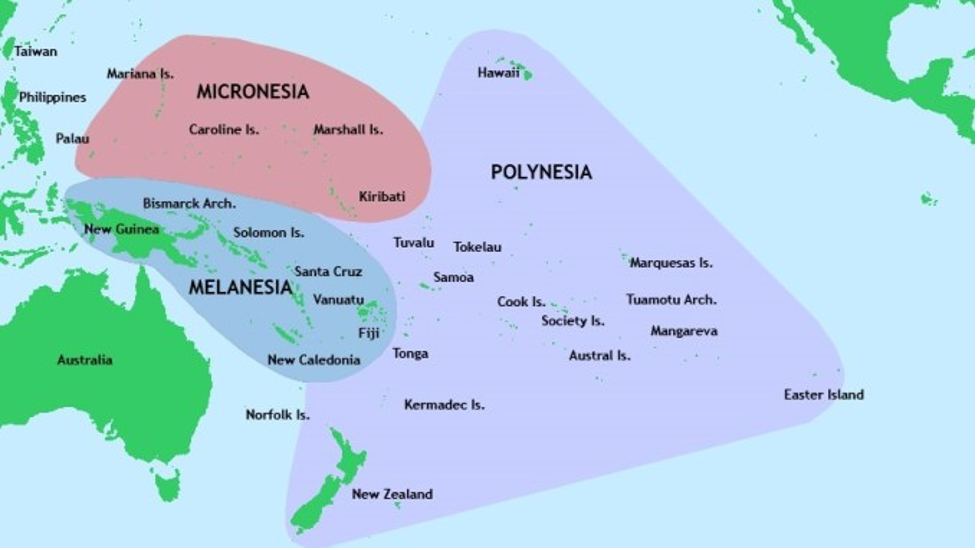
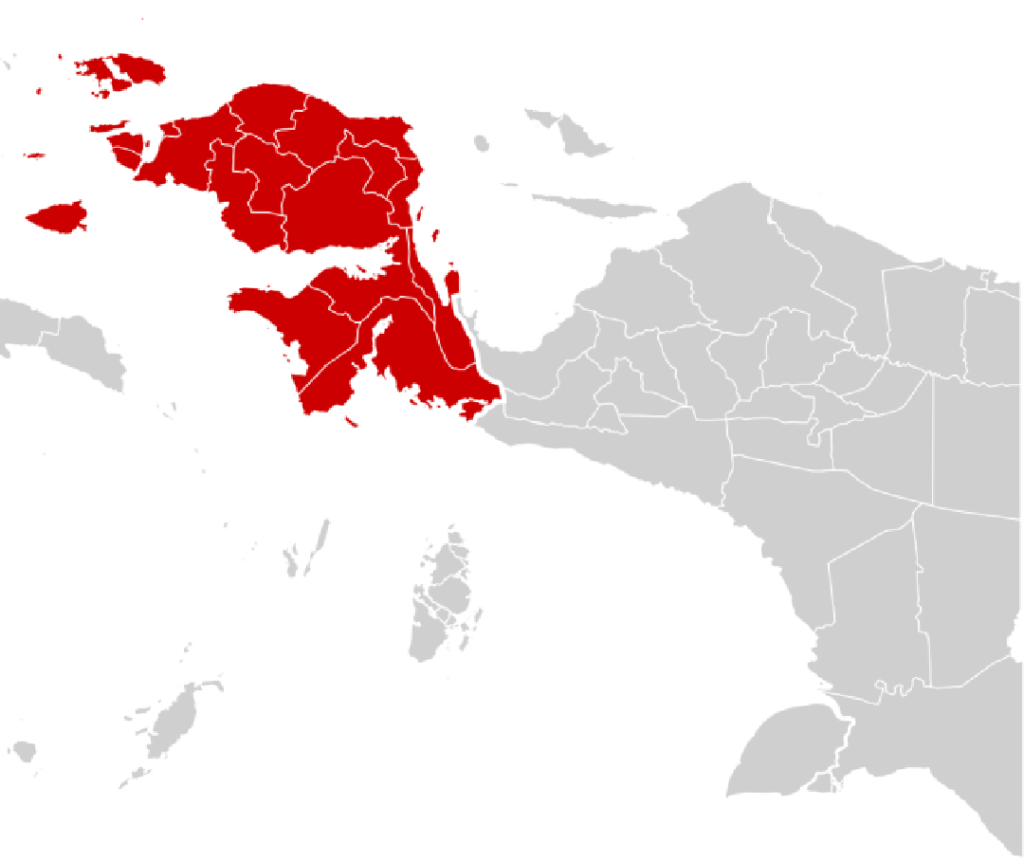
Talking about Papua and West Papua includes its indigenous people. The people of West Papua are known to be Melanesians, although there have been residents from outside the island living there, too.
How is the history of the Melanesians in the provinces? How did it all begin before they started inhabiting the island?
The Origin
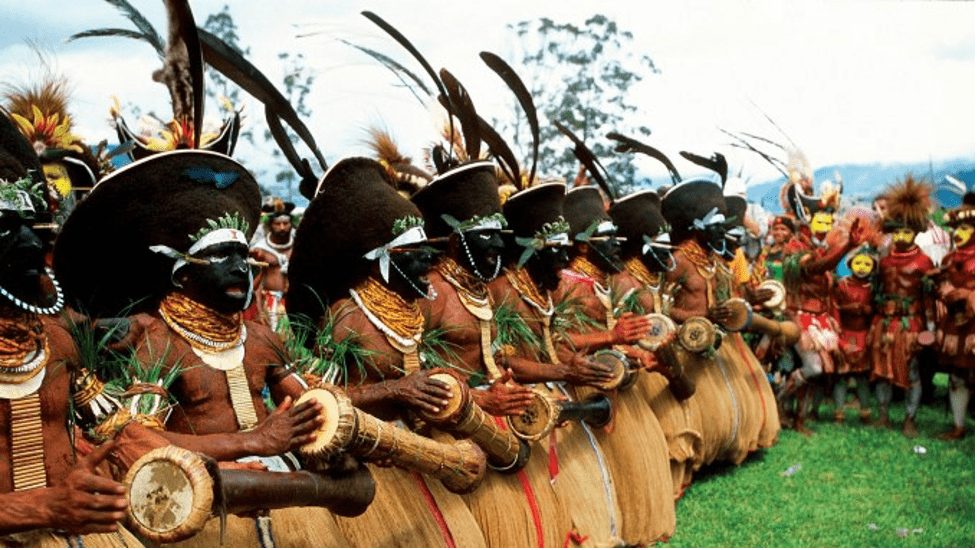

Actually, the Melanesians are not only in Papua and West Papua. They also live in Maluku Islands, Papua New Guinea, Vanuatu, and Fiji. The majority of Melanesians speak Austronesians, although there are those speaking other languages. Austronesian itself has several branches of sub-languages, which some are related to Papuan languages. Some of the other languages besides Austronesian language family include Tok Pisin, Hiri Motu, Bislama, Papuan Malay, and many more.
There have been various theories regarding the existence of the Melanesians in these provinces. Over 3000 years ago, the Austronesian people had migrated there and came in contact with the Papuan-speaking residents who had already been around.
However, that theory was later overturned in 2008 through a research study. This study was done after over 800 genetic makers among various Pacific people were evaluated. The study found that the Melanesians were not really genetically related to either Polynesians or Austronesians. Surprisingly, they were strongly related to the Taiwanese aborigines from East Asia.
Another theory and study later turned up in 2010. Svante Paabo, a Swedish geneticist, claimed that a certain ancient human species called “Denisova hominin” had come in contact with the Melanesian ancestors in Asia.
Other Theories Regarding The Indigenous Papuans
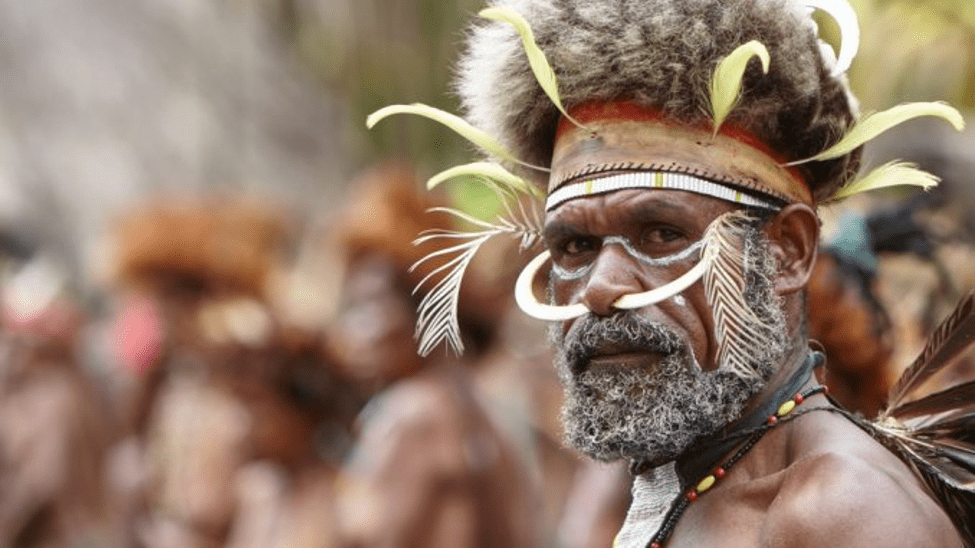

The debates and theories did not stop there. There are other theories regarding indigenous Papuans. These theories are:
- The first migration from the Malay Archipelago to New Guinea and Australia around 50,000 years ago
- The migration of the Austronesians from the north around 3,500 years ago. Not only Austronesian languages, but they were believed to have also introduced pigs to the locals.
The Ethnic Groups of West Papua
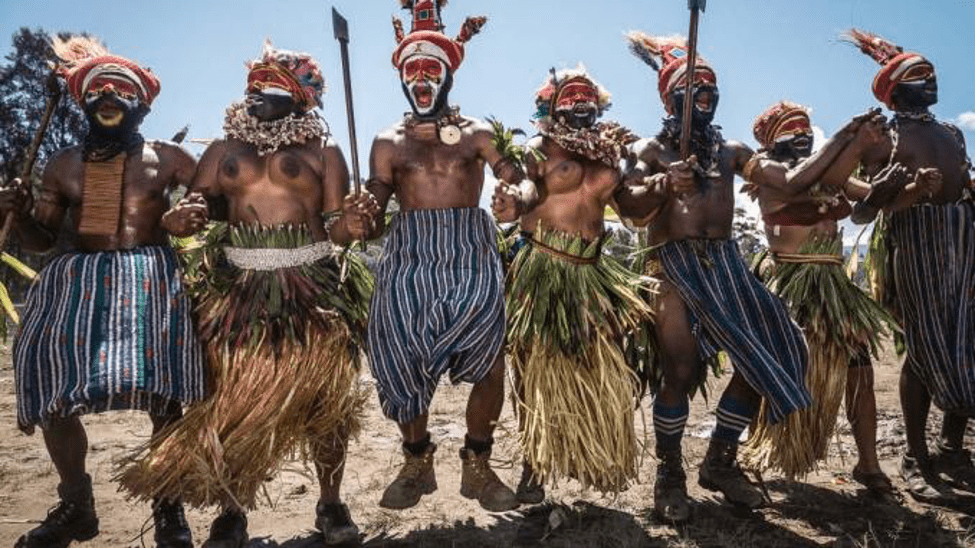

The people of West Papua might be famously known as the Melanesians. However, the indigenous people also have different ethnic groups here. The famous three are, of course, Asmat, Dani, and Lani.
- Asmat
Asmat is one of the three famous main ethnic groups in Papua and West Papua. When the topic of these provinces is mentioned, many people will automatically remember Asmat. Their home base is between Lorentz National Park and World Heritage Site. They are also famous for their woodcarving skills and business.
- Dani
Dani is also one of the three famous main ethnic groups in these provinces. They are also called “Ndani”. They reside in the highlands of Papua, including the Baliem Valley. The name “Ndani” is from the Moni people, although this ethnic group does not refer themselves to the name.
- Lani
The Lani have been misidentified as the “Western Dani” by the missionaries since they also live in the highlands of Papua. They are also related to Dani and Yali. They speak Lani language. Their ancestors had practiced animism. Some of the older Lani people may still be animistic, while the modern Lani people practice Christianity.
Other ethnic groups of West Papua
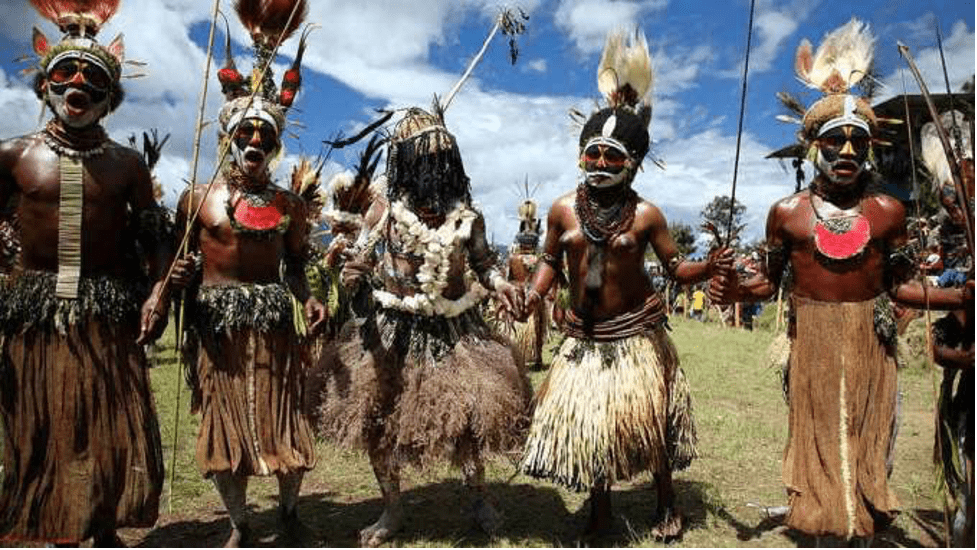

The Melanesians are so far divided into the three main ethnic groups above and more. There are also other ethnic groups besides them, which are Amung, Bauzi, Ekari, Fayu, Kombai, Koteka, Korowai, Marind, Mek, Moni, Sawi, Wolani, and Yali.
These other ethnic groups also have their uniqueness. The Amung speaks their language called Damal. The Bauzi, living in the north-central of Papua, used to live on hunting and gathering. Their ancestors were animistic, but the modern-day, Bauzi people practice Christianity.
The Ekari people are also called by other names, like Mee, Bunani Mee, The Ekagi, and Kapauku. The Fayu people have a unique tradition. Besides living in single-family groups, twice a year they gather to exchange brides.
The Kombai live in huts. Every clan lives in a large treehouse, but most of their daily activities are done outdoors. The Korowai people live in the southeastern of the province. Based on an old article in The Daily Telegraph, the Korowai people had not been aware of the existence of other people until the 1970s.
The Marind ancestors used to go headhunting, especially when there were wars between clans and with other tribes. That was before the Christian missionaries came, and the culture in Marind changed. The Moni people are also known by other names, such as the Migani, Megani, Jonggunu, or Djonggunu.
The Sawi or Sawuy people had the same old culture as the Marind. When they too started embracing Christianity, the headhunting practice had stopped.
Here is the short history of the Melanesians as the indigenous people of West Papua. There are still plenty to discover among them to get a better understanding of their cultures and lives as people.