Papua’s borderlands cover a lot of ground in eastern Indonesia’s deep rainforests and highlands, which are often very far apart. In the past, these rural border areas next to Papua New Guinea had bad roads, few job opportunities, and growth that wasn’t fair. But the Indonesian government is trying to change that by promising to improve the economy in the border districts of Papua.
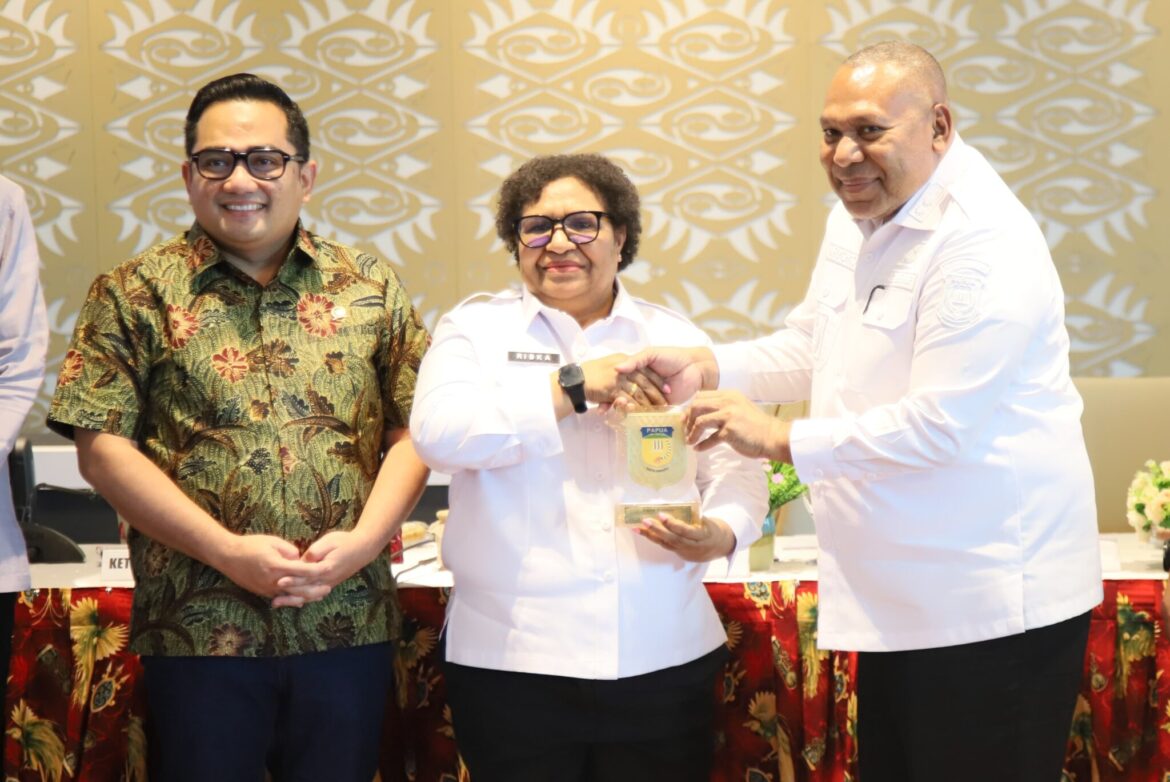
The main goal of this project is to turn border towns from places where people feel safe into places where the economy can grow. Ribka Haluk, the Deputy Minister of Home Affairs, made this vision clear in early 2026. This is part of President Prabowo Subianto’s bigger plan for growth. The goal of the policy is to make sure that Papua’s border towns have real economic growth, better infrastructure, and more social services.
A New Way for the Country to See Its Border Areas
Ribka Haluk sent a message on February 4, 2026, that changed how Indonesia thinks about its borders. On an official visit to Jayapura, she told members of parliament that border development had to mean more than just being free. Instead, she said, these places should be engines of economic growth for the people who live there.
Ribka says that people should stop thinking of cross-border posts, or Pos Lintas Batas Negara (PLBN), as just symbols of national defense. The government wants them to be places where people can work, get things done, and get help from the government.
President Prabowo has said that the big ministries should work together to come up with plans for growth in border areas. This vision is in line with that one. The President has asked the Ministry of Home Affairs, the Ministry of Finance, and the National Development Planning Agency to work with other groups to make sure that the economy grows and infrastructure is built at the same time.
The Strategic Importance of Papua’s Borders
Papua’s border areas are important for the country’s safety and economy. These places are like doors that let people from different countries trade and learn about each other’s cultures. But in the past, the economy has had trouble growing because it’s hard to get around and it’s far away from other areas.
Government officials think that making the economy better in these areas can help bring Papua closer to the rest of Indonesia. The goal of development projects is to make life better for native Papuan communities by creating jobs, helping local businesses, and raising the standard of living.
Experts say that Indonesia’s policy of decentralization is very important for the growth of its borders. Regional autonomy lets local governments carry out development projects that meet the needs of the people in their area. But for it to work, the central and regional governments need to talk to each other well.
Infrastructure as the Foundation of Economic Transformation
Building up infrastructure is still the most important thing that Indonesia is doing to help the economy along the border in Papua. In the last ten years, the government has spent a lot of money on roads, bridges, housing, and transit networks that connect faraway places to economic centers.
The Trans-Papua Highway is a huge network of roads that runs more than 4,300 kilometers from Sorong in the west to Merauke in the east. It is one of the most important projects that has had an impact. The road connects places that were cut off from each other before, making it easier for goods, health care, and education to get to rural areas.
Before the road was built, people could only get to villages by plane or boat. Now they can get there by car. Better connectivity makes it easier for people to get around and makes important things cheaper. Policymakers know that when they build new infrastructure, they have to be careful not to make things harder for people or the environment.
Building roads and bridges is just one part of investing in infrastructure. It also includes building homes, public buildings, and water resources. In the past, the government spent trillions of rupiah on building roads, homes, and water systems. This shows that Indonesia is very serious about helping Papua grow.
The Role of Special Autonomy Funds
Indonesia’s Special Autonomy framework is a big help to Papua’s economy as it changes. This way, Papua’s provincial governments will have more money and power to make decisions.
Ribka Haluk, the Deputy Minister, has said many times how important it is to use the Special Autonomy funds to their fullest so that development projects can get to places that are far away or on the border. The government has been paying more attention to things in the last few years. Officials are making sure that the money is used wisely and meets the needs of the area.
By 2025, the administration made sure that all of Papua’s provinces used all of the Special Autonomy money. People saw this milestone as a big step toward speeding up projects that build infrastructure and give people more economic power in the area.
New Autonomous Regions and Governance Reform
The creation of new self-governing provinces in Papua is another important part of Indonesia’s plan for growth. The goal of creating South Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, and Southwest Papua is to improve government efficiency and speed up the delivery of public services.
Ribka Haluk says that these new administrative bodies will help the central government give more specific help and advice in the first few years they are in charge. The new provinces have made plans for their long-term growth that include building infrastructure and making the economy more diverse.
There are also plans to make sure that native Papuans run the government in the region. Policies for hiring people put a lot of emphasis on hiring more native Papuans for civil service jobs. This is so that development projects reflect the views of the people who live there.
Economic Empowerment Through Local Enterprise
One part of Indonesia’s plan to improve its borders is to build infrastructure. Another part is to improve the economies of the areas along the border. People can start small and medium-sized businesses, village cooperatives, and farming projects that will help families make more money through these programs.
Officials in the government think that getting people to start their own businesses can help the economies of border areas by getting them to spend money. The goal of cooperative development projects is to help local fishing, farming, and crafts while also creating jobs that will last.
Economic empowerment is especially important in Papua, where traditional ways of making a living are still very important to community life. Policymakers want to make sure that everyone can take part in development by combining old and new ways of doing business with new systems that help businesses grow.
Border Posts as Places to Get into the Economy
Cross-border infrastructure is an important part of Indonesia’s plan to make changes. The PLBN buildings are being changed so that they can be used for more than just checking people in and out. They will also be used for work and services.
These facilities should make it easier for people to trade across borders in a legal way, bring in investment, and provide public services like education and healthcare in a way that works together. Officials say that the gap in wealth between communities along the border can slowly get smaller when they can use services and marketplaces.
The Indonesian government wants to make these changes as part of a bigger plan to make border towns the “front porch” of the country, a place of national pride and business instead of being cut off from the rest of the country.
Challenges and Logistical Obstacles
Even though a lot of progress has been made, it is still hard to build Papua’s border economy. It is hard to plan and build anything in this area because of its geography. This makes things more expensive and takes longer. It costs a lot more to build infrastructure in this part of Indonesia because of the mountains, thick woods, and few roads.
Experts say that organizations need to work together closely to avoid starting too many similar projects and to make sure that resources are used wisely. They also stress how important it is to include local communities in planning so that development projects meet real needs and get support from the people.
Balancing Development and Social Stability
In Papua’s border areas, there is a strong link between economic growth and social stability. Some people who make decisions think that making the economy better can help communities become stronger and less unequal.
Some politicians and community leaders have said that it’s very important to treat schools and hospitals like businesses. They say that if we want the economy to grow in a way that lasts, we need to invest in education, healthcare, and training our workers all at once.
This way of thinking says that more people are starting to realize that just having good infrastructure won’t make them rich. To make sure that people in the area get long-term benefits, building things and growing human capital must work together.
Integrating Border Development into National Strategy
Indonesia is helping Papua’s border economy as part of a larger plan for the whole country to encourage fair growth. People are starting to think of border areas as important resources that can help trade and bring people from different places together.
Indonesia wants to close the gap in development between cities and the countryside by spending money on infrastructure, economic projects, and changing how the government works. These efforts also help bring the country together by making sure that people in remote areas feel like they are a part of Indonesia’s economic success.
A Plan for the Future
People who live on the border of Papua see the government’s desire to make changes as both a chance and a duty. People are hopeful that their lives will get better and that they will be able to connect with the rest of Indonesia more easily because of better roads, trade facilities, and public services.
Politicians have a hard time making sure that big projects have effects that last. There needs to be ongoing funding, a strong government, and community involvement to make the border better.
Ribka Haluk, the Deputy Minister, has said many times that it will take a long time to improve the economy in Papua’s border areas. Changing the social and economic situation in one of Indonesia’s most troubled areas is a long-term national goal.
Conclusion
Indonesia’s work to improve Papua’s border economy is a big change in how the country is growing. The government wants to make growth more inclusive in one of the country’s most remote areas by turning border checkpoints into business centers, building more infrastructure, and giving local people more power.
There are still problems to solve, but the fact that central and regional governments are still working on them shows that they really want to close the gaps in development and make the country more connected. If it works, Papua’s border districts could go from being isolated frontiers to busy gateways to economic opportunity. This would show how strategic investment and inclusive governance could change what development means in the easternmost parts of Indonesia.